Picture a future where preterm babies can grow properly outside the body or where couples struggling with infertility have an alternative means of creating a family. It is no longer science fiction material. Artificial wombs refer to ectogenesis, and while this reproductive technology and neonatal advancement are not available yet, answers about their implications on society and the future of human reproduction have not been answered. Here, we will explore the nature of artificial wombs, how they work, their possible benefits, and their ethical and societal importance.
What is an Artificial Womb? (Revolutionizing Reproductive Technology)
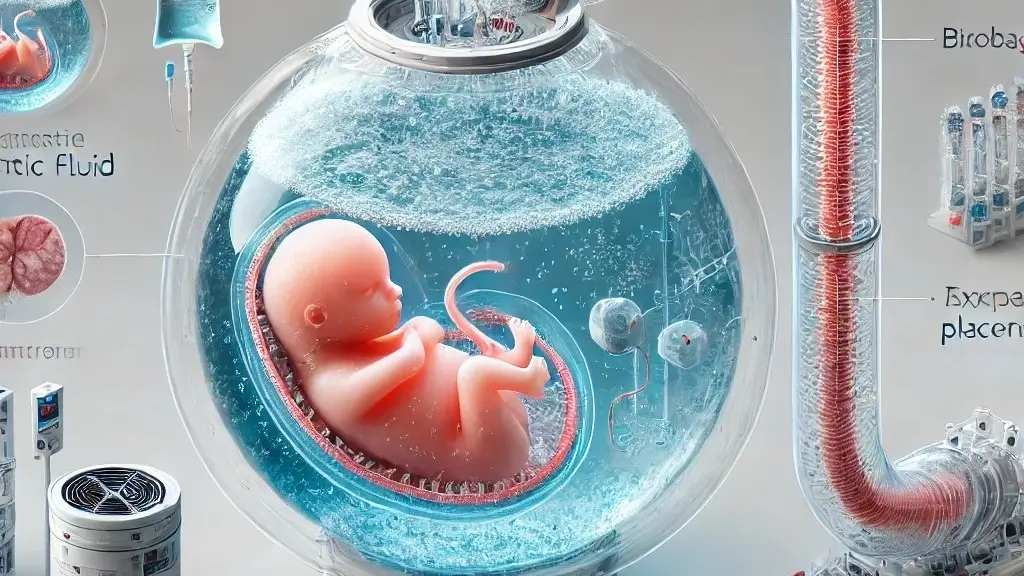
An artificial womb is a device that tries to duplicate the natural surroundings of a mother’s womb, enabling a fetus to grow and develop outside the human body. Whereas traditional incubators nurture preemies after birth, artificial wombs develop a simulated environment that mimics the experience of pregnancy itself. This environment supplies oxygen and nutrients, regulates temperature, and protects the developing fetus from external damage.
A high-tech replacement womb is a controlled, clean environment where all the conditions required for fetal growth are carefully monitored and maintained. Although such concepts sound like science fiction, researchers are already actively converging.
The Science Behind Artificial Wombs: How Ectogenesis Works
Then, there is the ongoing problem of developing an artificial womb from the ground up. Here are the key pieces and how they interact:
1. Biobag or Fluid-Filled Container
The artificial womb is usually a clear, fluid-filled chamber known as a “biobag.” The device consists of an artificial womb-like container that is filled with synthetic amniotic fluid, which covers up the fetus, preventing it from being exposed to the outside world, much like during a normal pregnancy.
2. Oxygenation and Nutrient Delivery
An artificial placenta supplies oxygen and nutrients directly to the fetus’s bloodstream. This technology acts like a mother’s placenta, ensuring the growing fetus gets everything it needs to develop.
3. Temperature Control
Temperature is everything when it comes to fetal development. These artificial wombs have precise temperature control systems to maintain a constant environment.
4. Waste Removal
Just as one of the placenta’s functions is to sweep away waste products from a fetus’s bloodstream in natural pregnancy, artificial wombs employ specialized systems to “keep the fetus healthy and in balance” as well.
5. Monitoring and Feedback Systems
Refined sensors help monitor the fetus’s vital signals, including heart rate, oxygen levels, and growth progress, in real-time, ensuring that the fetus stays within optimal parameters.
Potential Benefits of Artificial Wombs
There are many transformative possibilities in the use of artificial womb technology. Some of the top benefits include the following:
1. Improved Outcomes for Premature Infants

A Safer Environment: Premature birth is fraught with risks, including underdeveloped lungs and brain damage, as well as infections.
- There are about 15 million preterm births each year in the world, and they are the leading cause of death for children younger than five, according to the World Health Organization. That is a leading global health crisis that artificial wombs can already help with by enabling babies to develop in a better environment, as well as paving the way for more neonatal technology to bring down the infant mortality rate. Read more about the worldwide burden of premature births on the World Health Organization’s website. Deploying artificial wombs could create a safer, more stable environment where these infants could continue developing.
- Reduced Mortality Rates: Artificial wombs can help premature babies survive and grow healthier by acting like a natural womb. Caring for a premature baby in a hospital costs $3,000–$5,000 per day in rich countries. Artificial wombs could lower these costs by reducing hospital time.
2. Expanded Reproductive Options
- For Individuals with womb Issues: Individuals who cannot carry a pregnancy because of health conditions or previous surgeries could use them to have biological children.
- For Same-Gender Couples: The availability of artificial wombs could allow same-gender couples to reproduce without the use of a surrogate, allowing for more independence and discretion in the reproductive process.
3. Advancement in Neonatal Care
Artificial womb technology may revolutionize upper care by providing completely novel forms of medical treatment and care for high-risk pregnancies. Research has shown that artificial womb technology designed to avoid complications associated with preterm births could significantly reduce the cost of using neonatal intensive care units, saving healthcare systems billions of dollars each year.
Ethical and Social Considerations
Artificial wombs provide advantages but involve complex ethical and societal implications. Here are some of the most significant issues:
1. Ethical Debates
- When Does Life Begin? Artificial wombs also do away with traditional definitions of birth and viability, raising questions about when a fetus should qualify as a legal person.
- Parental Roles: How will artificial wombs redefine maternal pregnancy and parental responsibility?
2. Accessibility and Equity
- Who Will Have Access? If artificial wombs are costly, will they mean people will be forced to compete to have wealthier parents, intensifying existing inequalities?
- Global Disparities: How can we ensure that people in low-income and developing countries benefit from this technology?
3. Social Implications
- Impact on Traditional Pregnancy: When artificial wombs are widely available, how will they change societal attitudes towards the natural process of pregnancy and motherhood?
- Potential for Misuse: Might artificial wombs lead to unethical applications, like “designer babies” or overpopulation?
Current Research and Developments
Artificial womb technology is progressing quite rapidly as researchers worldwide are working on developing it further. Here are some highlights
- 2017: Scientists at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia used a “biobag” to support the development of premature lambs. The lambs developed normally inside the artificial womb for several weeks, a significant milestone. To learn more, see the study summary at Science Daily.
- Human Trials: The construction of an artificial womb for a human fetus has not yet been attempted. However, a few research groups are moving toward ethical and regulatory approval for such studies in the coming years.
- Technological Inventions: Better materials, artificial placentas, and monitoring systems are helping the field advance faster, making real-world use possible soon.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its promise, artificial womb technology has several obstacles:
1. Technical Hurdles
- Complexity: Mimicking a natural uterus’s complex functions is challenging and requires significant innovation.
- Safety: The long-term safety and health of fetuses grown in artificial wombs is paramount.
2. Regulatory and Ethical Barriers
- Approval Processes: That said, getting human trials approved is a complicated maze of regulations and debates around ethics.
- Public Acceptance: It will require time and education to convince society that artificial wombs are a safe and ethical option.
3. Cost and Accessibility
- High Costs: Developing and implementing artificial womb technology is expensive, which could limit its accessibility.
- Rising: Making this technology available globally will require substantial investment and partnership.
The Future of Artificial Wombs: Ectogenesis and Beyond
Artificial wombs have the potential to reshape not only reproductive medicine but also society as a whole. Here are some possibilities:
- Reducing Infant Mortality: Artificial wombs could save the lives of countless premature babies and improve their long-term health outcomes.
- Revolutionizing Fertility Treatments: From same-gender couples to individuals with fertility challenges, artificial wombs could offer new paths to parenthood.
- Transforming Societal Norms: As artificial wombs become more common, they may challenge traditional ideas about pregnancy, parenting, and family structures.
Conclusion
Artificial wombs are a breakthrough in science and medicine. They offer hope for premature babies, support ectogenesis (growth outside the body), and could change the future of reproduction. However, as this technology evolves, so do essential ethical, social, and regulatory questions that must be tackled. How do you feel about the idea of artificial wombs? Could they improve society in ways we can’t yet imagine, or do they create dangers we are not ready to face? As we are on the verge of this technological advancement, we are having the most critical conversation on its wisdom.